Carbon Credits
A carbon market allows investors and corporations to trade both carbon credits and carbon offsets simultaneously.
New Revenue Streams
No Added Costs
Setting the Example
Value Add
How It Works
Always Adding Value
AgriGold Capital’s business model is to constantly find ways to add value to California ag land. Carbon credits are one way we separate ourselves from typical firms.
Each deal is chosen with the plan to sell the carbon credits generated by that land to the open carbon marketplace. This increases returns for our investors and the environment.
‘Carbon credits are a simple way to help ensure consistent, excellent returns for our investors.’
Joshua Lagan
CFO

Carbon Markets

When it comes to the sale of carbon credits within the carbon marketplace, there are two significant, separate markets to choose from.
- One is a regulated market, set by “cap-and-trade” regulations at the regional and state levels.
- The other is a voluntary market where businesses and individuals buy credits (of their own accord) to offset their carbon emissions.
California Market
In the United States, no national carbon market exists, and only one state – California – has a formal cap-and-trade program.
Company Incentives
When companies meet their emissions “cap,” they look towards the regulatory market to “trade” so that they can stay under that cap.
Carbon Market Data
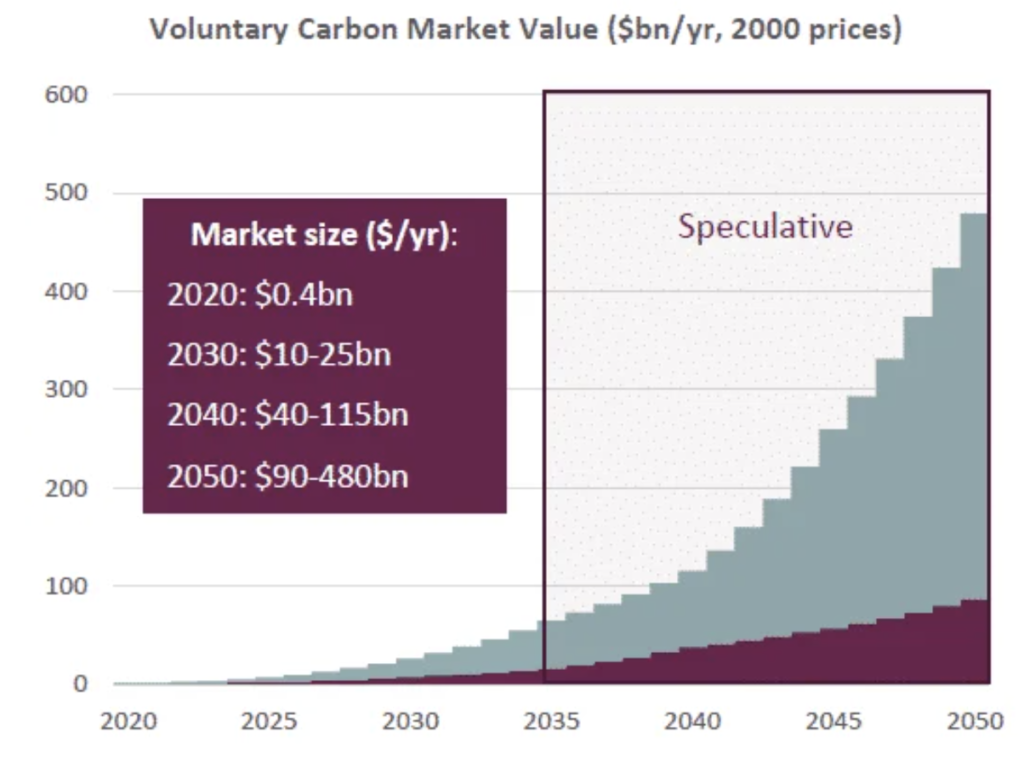
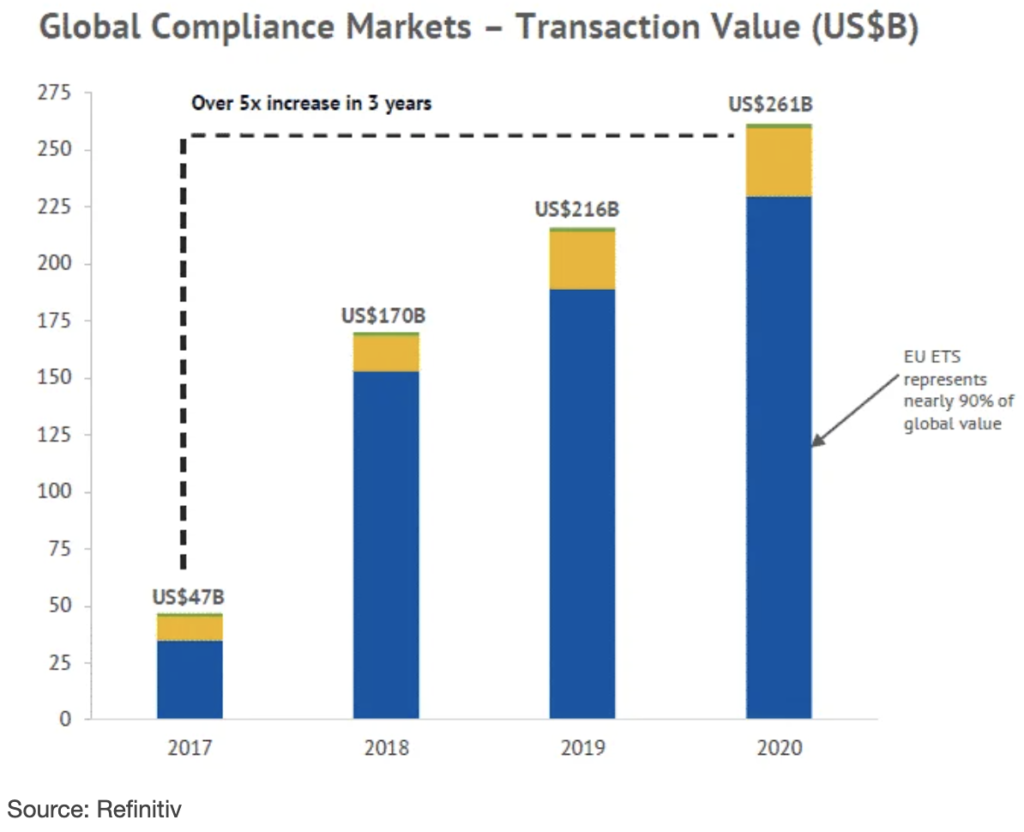
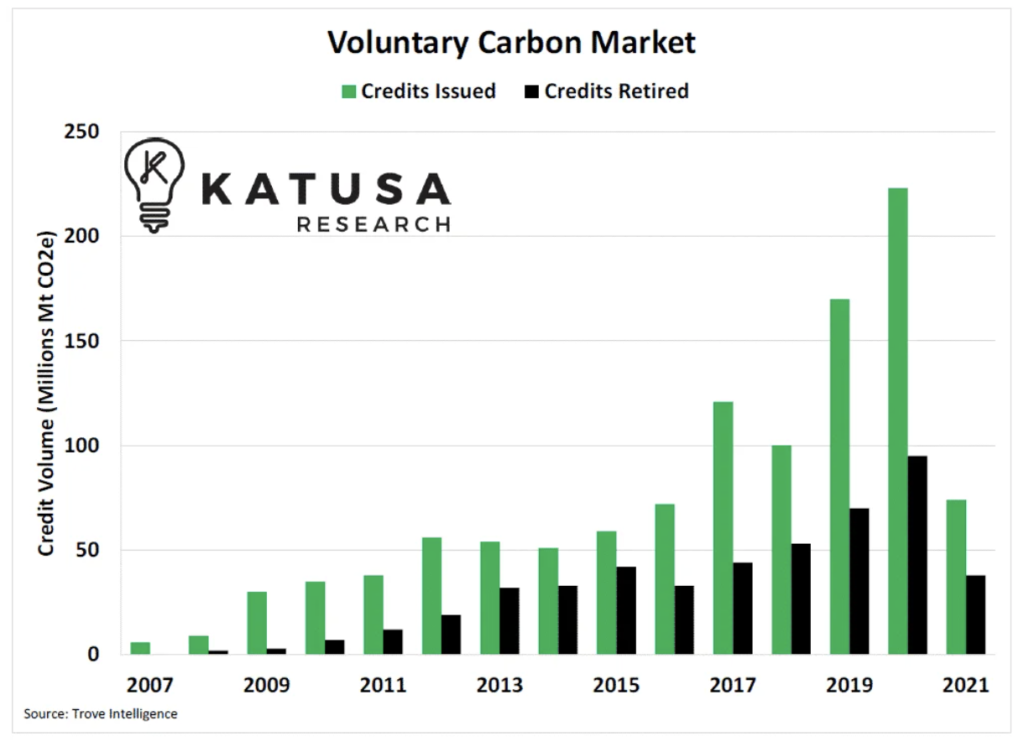
Frequently Asked Carbon Credit Questions
How Much Does a Carbon Credit Cost?
Carbon credits are priced differently depending on the location and market where they’re traded. The average price for carbon credits was $4.33 per ton in 2019. This figure spiked to as much as $5.60 per ton in 2020 before settling to an average of $4.73 in the first eight months of the following year and reaching an average of $6.97 per ton in 2023.
Who Can Sell Carbon Credits?
A diverse range of enterprises and individuals can sell carbon credits, depending on their ability to participate in a carbon registry or sequestration program. Landowners may be able to sell carbon credits if they enroll their land—be it forest, grassland, or rangeland—into a project, which will then measure and pay for carbon stored. Landowners may then earn additional revenue from the sale of credits linked to their land stewardship. Typically, the project operator will also collect a broker fee.
Where Can Carbon Credits Be Bought?
Several private companies offer carbon offsets to companies or individuals seeking to reduce their net carbon footprint. These offsets represent investments or contributions to forestry or other projects with a negative carbon footprint. Buyers can also purchase tradable credits on a carbon exchange such as New York-based Xpansive CBL or Singapore’s AirCarbon Exchange.
What Makes a Good Carbon Credit Project?
At a minimum, high-quality carbon credit projects will be audited by an accredited, third-party verifier and meet specific criteria dictated by internationally-recognized standards bodies. These criteria include additionality, detailed quantification of the greenhouse gas reduction or removal activity as compared to a baseline, and permanence. There are many different types of carbon projects that are eligible to generate carbon credits as long as they adhere to the requirements of methodologies that have been approved by the standards bodies. Furthermore, voluntary carbon projects can be found in many countries across the globe.
© Copyright 2024. All rights reserved.
